Peer Reviewed
News
01 Jan 2024
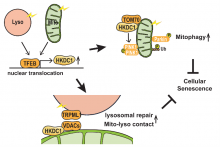
Researchers from Osaka University have shown that a protein called HKDC1 is a new target of another protein, TFEB, and plays key roles in maintaining the stability of both mitochondria and lysosomes. HKDC1 is essential for mitophagy to remove damaged mitochondria, and mediates mitochondria–lysosome contact, which is critical for lysosomal repair. The role of HKDC1 in maintaining the stability of these organelles counteracts cellular senescence, revealing HKDC1 as a potential therapeutic target for age-related diseases.
28 Dec 2023
An international research group has engineered a novel high-strength flexible device by combining piezoelectric composites with unidirectional carbon fiber. The new device transforms kinetic energy from the human motion into electricity, providing an efficient and reliable means for high-strength and self-powered sensors.
28 Dec 2023
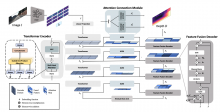
Researchers have developed a high-speed, high-sensitivity terahertz-wave detector operating at room temperature, paving the way for advancements in the development of next generation 6G/7G technology.
26 Dec 2023
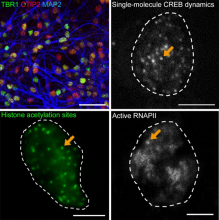
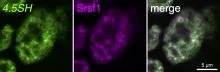
Researchers from Osaka University and Shenzhen Bay Laboratory found that neuronal activity induces gene expression at sites of acetylation by promoting the emergence of cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), CREB binding protein (CBP), and RNA polymerase II. These proteins are targeted to the appropriate sites by CBP-mediated histone acetylation at activity-dependent gene loci.
26 Dec 2023
- Professor Sunghoon Im's team at DGIST has developed depth-sensing technology that can be reliably used in diverse environments by analyzing the relationship between the neural network structure and distance sensing in autonomous driving.
- The new technology is expected to contribute to the development of a wide range of AI fields, such as autonomous driving, which must be performed safely in various urban settings and weather conditions
26 Dec 2023
- Professor Kyung-In Jang’s research team at DGIST has developed a complex taste sensor that mimics the gustatory system and detects saltiness, sourness, bitterness, and sweetness in real-time.
- It is expected to be applied in various fields, including the food, cosmetics, and medicine industries
25 Dec 2023
Kavli IPMU researchers are part of a team that has shown it is possible to image small animal tissue clearly to several hundred micrometers using multi-probe imaging.
25 Dec 2023
Researchers employ common plastics to kickstart radical chain reactions, creating a way to reuse plastic waste while improving process safety and efficiency.
22 Dec 2023
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University assessed the correlation between human mobility restrictions and the medical costs associated with lifestyle-related diseases during the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan. A cross-sectional study revealed that an increase in walking and public transit use was associated with reduced medical costs of lifestyle diseases. These findings implicate governments to take measures other than restricting walking and public transit during pandemics and emphasize the importance of walkable cities.
22 Dec 2023
Researchers from Osaka University developed a bio-logger for seabirds that enables long-term observation of rare behaviors. The bio-logger employs low-power depth sensors and accelerometers to identify rare behavior using a light-weight outlier detection model and records the behavior in a 5-min video. Observations using the bio-loggers on Streaked Shearwaters revealed novel aspects of head-shaking and foraging strategies. This approach will enable a wider range of animal behaviors in various environments to be observed.
21 Dec 2023
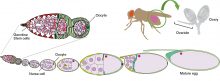
A research group led by Osaka University and University of Hawaii Manoa found that in female fruit flies, microorganisms enhance reproductive function, boosting the number of cells that form eggs and the number of mature eggs. This is done by controlling the release of hormones to speed up cell division in the ovaries, and limiting programmed cell death. These findings could improve reproductive medicine and could aid the development of new methods to enhance fertility.
21 Dec 2023
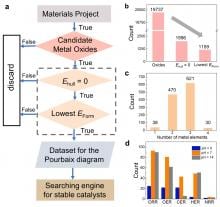
Identifying low-cost metal oxide electrocatalysts is essential to help us wean ourselves off fossil fuels. Yet doing so is a time-consuming process, with lots of trial and error required. A group of researchers has explored how data mining can be employed to help speed up this process.
21 Dec 2023
A team of researchers has developed an innovative method to design complicated all-α proteins, characterized by their non-uniformly arranged α-helices as seen in hemoglobin. Employing their novel approach, the team successfully created five unique all-α protein structures, each distinguished by their complicated arrangements of α-helices. This capability holds immense potential in designing functional proteins.
21 Dec 2023
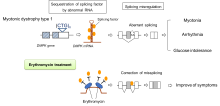
In a phase 2 trial, researchers from Osaka University have found that erythromycin, a commonly used antibiotic, has acceptable safety and tolerability profiles in patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1. This common form of muscular dystrophy currently has no cure, and the research team is hopeful that phase 2b and 3 trials will further reveal the efficacy of erythromycin as a treatment—at least in some patients.
21 Dec 2023
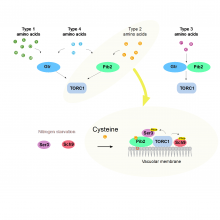
Researchers from Osaka University have discovered how amino acids activate a key cell, TORC1, which is a master regulator in living organisms that controls whether cells grow or recycle their contents in yeast. Notably, the team found that the amino acid cysteine is sensed by a protein called Pib2 and that the two bind together to trigger TORC1. This is important because faulty TORC1 has been linked to disease such as cancer.
21 Dec 2023
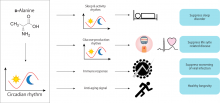
Researchers from Osaka University have shown that the rare D-form of the amino acid alanine shows a clear circadian rhythm, and is able to affect the circadian clock and regulate gluconeogenesis, a method of glucose release, in the kidney. D-alanine upregulates genes linked to both gluconeogenesis and the circadian rhythm through the circadian transcriptional network. D-alanine is linked to many metabolic and immunological diseases, and this mechanistic insight could potentially lead to novel therapeutic approaches.
20 Dec 2023
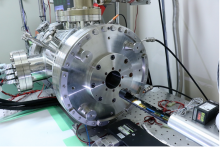
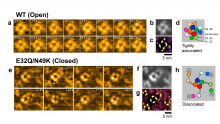
Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University report in Nature Communications a high-speed atomic force microscopy study of the structural dynamics of sodium ion channels in cell membranes. The findings provide insights into the mechanism behind the generation of cell-membrane action potentials.
20 Dec 2023
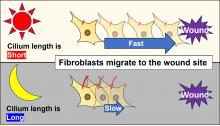
We’re all familiar with our body’s internal clock: it gives us cues on when to wake and when to rest, but it also can determine the rate and time of day at which your body most effectively heals wounds.
19 Dec 2023
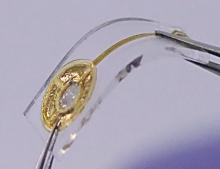
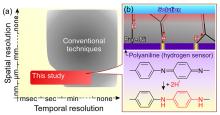
Using conventional X-rays and lasers to detect the atomic state of hydrogen is challenging, given its small size. A group of researchers may have overcome this barrier by unveiling a new visualization technique that employs an optical microscope and polyaniline to paint a better picture of how hydrogen behaves in metals.
19 Dec 2023
A research team at Osaka Metropolitan University has fabricated a gallium nitride (GaN) transistor using diamond, which of all natural materials has the highest thermal conductivity on earth, as a substrate, and they succeeded in increasing heat dissipation by more than two times compared with conventional transistors. The transistor is expected to be useful not only in the fields of 5G communication base stations, weather radar, and satellite communications, but also in microwave heating and plasma processing.
19 Dec 2023
SUTD researchers developed an advanced system of breast cancer cell detection with improved speed and sensitivity, using a viral mechanism to enhance the tool’s sensing accuracy.
18 Dec 2023
Researchers identify RBFox1 as a key intrinsic regulator of heart muscle cell maturation, overcoming a major limitation in cardiac regenerative therapy and disease modelling and demonstrating for the first time that RNA splicing control can significantly impact this process.
15 Dec 2023
Riding the momentum of the environment-aware agenda, SUTD researchers were part of an international collaboration that developed a sustainable approach to discover and identify materials for next-generation electronics.
13 Dec 2023
A previously mysterious small RNA molecule in mice is found to play a crucial role in gene expression, and may be the first identified member of a new class of regulatory RNAs.
13 Dec 2023
Scientists at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed an efficient, non-invasive, and pain-free method to generate canine-induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). They identified six reprogramming genes that can boost canine iPSC generation by 120 times compared to conventional methods using fibroblasts. The iPSCs were created from urine-derived cells without the need for feeder cells, an impossible feat until now. Their findings are expected to advance regenerative medicine and genetic disease research in veterinary medicine.
12 Dec 2023
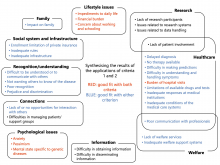
Researchers from Osaka University created an online space for conversation, collaboration and knowledge sharing among patients with rare diseases, their families, researchers and policymakers. A series of workshops generated evidence that could contribute to new policies in the field of rare diseases and explore ways that stakeholders could be involved in the process.
12 Dec 2023
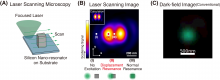
Researchers from Osaka University and collaborating partners have developed a new means of manipulating Mie scattering from nanostructures. By judicious choice of the laser illumination position with respect to the center of a nanostructure, one can strongly enhance optical responses that would not have been otherwise possible. This work is an important milestone in modern meta-photonics and will benefit computing and communication technologies.
11 Dec 2023
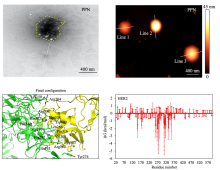
Asteroids offer valuable windows into the early solar system, given that they are remnants of planetary embryos that failed to form into planets. A recent analysis of samples from Ryugu offered insights into the composition of water- and carbon-rich small bodies in the solar system.
08 Dec 2023
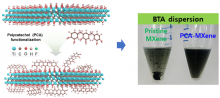
- Professor Jong-min Choi’s research team at DGIST develops a stabilization technology that simultaneously increases efficiency and stability by applying MXene to quantum dot photovoltaic cells
- The introduction of MXene is expected to improve the performance of various electronic devices
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.