Health
News
28 Mar 2023
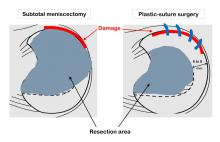
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Medicine conducted an interoperative comparison of lateral disc meniscus injuries of young patients (aged 15 or less), that were treated with plastic sutures or subtotal resection, to see if there was a difference in postoperative cartilage degeneration. The research group observed that sub-total meniscectomies were more likely to show cartilage degeneration, being worst in lateral disc meniscus injuries. In addition, they found that even with higher levels of meniscus damage, preserving the meniscus with sutures was more effective in protecting the cartilage in young patients.
28 Mar 2023
· Duke-NUS sleep scientists’ analyses show associations between early classes, less sleep, poor attendance and reduced grade point average.
· Studies in secondary and junior college students have shown that later start times can have positive impacts on grades.
27 Mar 2023
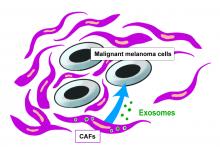
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are key factors in the tumor microenvironment, which have been implicated in cancer cell progression. It has also been reported that vesicles called exosomes produced by these CAFs play an important role in cancer progression. An Osaka Metropolitan University research group investigated the effect of CAF-derived exosomes on the growth of malignant melanoma cells. They found that CAF-derived exosomes express CD9 and CD63 transmembrane proteins, and that the CD9-positive exosomes may inhibit the growth of malignant melanoma cells.
27 Mar 2023
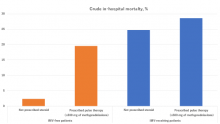
Researchers from Osaka University have found that repeated high-dose treatment, known as pulse therapy, with the steroid methylprednisolone reduces in-hospital deaths in COVID-19 patients who receive invasive mechanical ventilation, but not in patients who don’t receive invasive mechanical ventilation. These findings were only possible using appropriate statistical methods to remove bias from the data, which originally seemed to show that the opposite was true. These results can improve patient treatment and reduce COVID-19-related deaths worldwide.
24 Mar 2023
Hailey-Hailey disease is a rare, inherited condition characterized by patches of blisters appearing mainly in the skin folds of the arm pits, groin and under the breasts. It is caused by a mutation in the gene that codes for a specific protein. Tohoku University scientists have uncovered some critical details of this protein’s structure, and the findings could build the foundation for developing treatment for Hailey-Hailey disease and other neurodegenerative conditions.
23 Mar 2023
A research group from Osaka Metropolitan University investigated the relationship between tobacco use, including heated tobacco products, with the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19. The researchers administered an online survey of living conditions in February 2022 to 30,130 participants aged 16-81 years, finding that heated tobacco product users had significantly higher rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to non-tobacco users. Furthermore, the research group found that among all tobacco users, those who used both heated tobacco products and traditional cigarettes had the highest incidence of requiring hospitalization or oxygen due to COVID-19.
23 Mar 2023
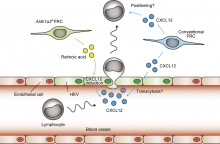
Researchers from Osaka University identified a subset of fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) that simultaneously express two proteins, Aldh1a2 and Tie2, making them unique to areas of the omentum called milky spots. Genetic depletion of these cells caused structural disruption of milky spots. The FRCs were critical to the abdominal immune system as they regulated CXCL12 levels, a molecule necessary for lymphocyte recruitment from blood circulation. These insights can help develop novel treatments for intra-abdominal infections.
21 Mar 2023
Consumer choices in an experimental online grocery store indicate the likely impact of a new labelling system in Singapore.
20 Mar 2023
Scientists from Alliance University, Bangalore, Birla Institute of Technology Mesra, Inha University, Hanyang University, South Korea, and Newcastle University in Singapore have developed a new and straightforward approach to turn used COVID-19 facemasks into potential absorbent materials that can be employed for carbon capture from atmosphere.
18 Mar 2023
Scientists restore impaired kidney for the first time, How fibre composite fails when wet, Cleaner fish recognize themselves in pictures 🖼️🐟& The source of black carbon in the sea. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice. Plus our magazine Asia Research News 2023 is out now 🎉!
16 Mar 2023
PAXLOVID™ rollout continues with Laos, Malawi, Rwanda and Zambia as international access to oral treatments improves.
16 Mar 2023
Annual innovation event brings together global innovators, entrepreneurs, researchers and scientists, and experts from various fields and industries to showcase their latest innovations, share ideas, and collaborate with industries to develop better technologies and solutions to shape our future. This is also a platform for innovators to meet potential investors and partners.
15 Mar 2023
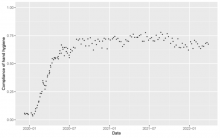
An Osaka University study investigated how the COVID-19 onset and media coverage affected hand hygiene compliance. Voluntary use of hand sanitizer in a hospital rose from 5% in December 2019 to 70%+ by August 2020. In the same period, TV coverage reached 7.7 hours/day on a national broadcaster. The study’s simulations found a significant relation between TV coverage and hand hygiene compliance, though no correlation between compliance and newly confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths.
15 Mar 2023
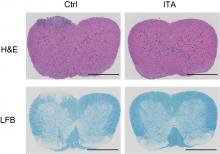
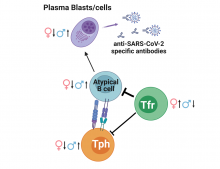
Researchers have revealed the modulatory effect of the anti-inflammatory metabolite itaconate on T helper and T regulatory cells, which may lead to new therapeutic approaches to treating some autoimmune diseases.
10 Mar 2023
Asia Research News monitors the latest research news in Asia. Some highlights that caught our attention this week are how hanging out with friends can keep you healthy, eggs made from male mice, and taking one step closer to a machine that can read our minds.
10 Mar 2023
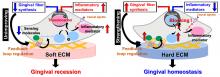
Tohoku University researchers have discovered that softer gums hinder the development of gingiva fibroblasts – the cells that help produce the fibers that hold our teeth in place.

09 Mar 2023
Cancer metastasis is a major cause of cancer-related death. A research team at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently identified a protein that triggers the migration of liver and pancreatic cancer cells and metastasis, and is correlated with shortening the survival time of patients. The research findings were verified by in vitro and in vivo models, supported with clinical data, and are expected to provide a new potential target for cancer therapy.
03 Mar 2023
Asia Research News monitors the latest research news in Asia. Some highlights that caught our attention this week are that COVID is transmissible between dogs, a new material created to replace extracted teeth, and a fungi-eating plant that was thought to be extinct.
02 Mar 2023
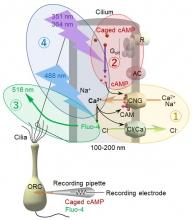
Researchers from Osaka University found that Ca2+ signaling simultaneously performed signal amplification and olfactory adaptation. The results demonstrated that this mysterious phenomenon was segregated inside the cilium. A novel system was used to observe changes in Ca2+ dynamics inside the thin structure of a cilium. Unveiling the mystery of Ca2+ signaling segregation further clarifies the mechanisms underlying the human sense of smell.
01 Mar 2023
Brain shrinkage patterns tied to low trust have links to depression vulnerability that can alert to its early detection even before symptoms appear.
24 Feb 2023
Asia Research News monitors the latest research news in Asia. Some highlights that caught our attention this week are a robotic hand with a magic touch, a solution to reduce the negative effects of screen time in children, and a team charting dung beetles.
24 Feb 2023
A research group from the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Medicine conducted a survey of 285 patients regarding the long-term aftereffects of COVID-19. As a result, they revealed that more than half of COVID-19 patients still had residual symptoms, even close to a year afterward. It became clear that fatigue, abnormalities in senses of taste and smell, hair loss, and sleep disorders could persist, regardless of the severity of the initial COVID-19.
23 Feb 2023
Scientists from Oil Crops Research Institute (OCRI) of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), Anhui Agricultural University (Anhui, China), Newcastle University in Singapore, and Huizhou Comvikin Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Guangdong, China) have developed a green and efficient approach to synthesize highly liposoluble and antioxidant L-ascorbyl esters by immobilized lipases.
21 Feb 2023
Sifting through sewage for SARS-CoV-2 genetic material could help authorities tailor infection control policies.
17 Feb 2023
Asia Research News monitors the latest research news in Asia. Some highlights that caught our attention this week are the discovery of a dinosaur larynx, 3D-printed contact lenses that use AR, and a leggy robot spider that can fly.
17 Feb 2023
Antimicrobial resistance is a global public health threat. Asia Research News has prepared a resource for journalists to find stories and connect with scientists combating antimicrobial resistance.
16 Feb 2023
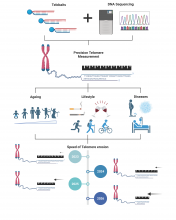
A new approach that ‘baits’ the caps or telomeres protecting the ends of chromosomes could provide information on how rapidly we are ageing and what we need to do to slow it down.
13 Feb 2023
Researchers from Osaka University have shown sex-specific differences in the immune response to COVID-19 infection. By identifying and analyzing the immune cell population in COVID-19 patients, they showed that infection results in a reduced ratio of circulating follicular T regulatory (cTfr) cells to a network of antibody-producing proteins, correlated with dysregulated antibody production. This cTfr cell reduction is more significant in males, providing cellular evidence for the observed association between increased risk and male sex.
09 Feb 2023
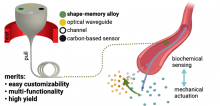
A research team led by an associate professor at Tohoku University has developed a microscopic fiber equipped with actuators and biochemical sensors. The breakthrough could be used to develop smart catheters and lead to further advancement in robotics.
02 Feb 2023
Blocking an immune-regulating protein reverses the damage caused by acute and chronic kidney disease, a preclinical study suggests.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Giants in history
Vietnamese surgeon Tôn Thất Tùng (10 May 1912 – 7 May 1982) developed a pioneering technique that reduced the risks and mortality rate of liver operations.
Chinese biochemist Chi Che Wang (1894 - 1979), one of the first Chinese women to study abroad, advanced to prominent research positions at American institutions including the University of Chicago and the Northwestern University Medical School.
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Flora Zaibun Majid ( 1939–2018) was an accomplished Bangladeshi researcher in botany and nutrition science and the first female chairperson of the Bangladesh Council of Scientific and Industrial Research.
Iranian physician and bacteriologist Azar Andami (8 December 1926 – 19 August 1984) developed a cholera vaccine to combat an outbreak that swept through the Middle East, India, Southeast Asia, and Africa in 1937.
Irene Ayako Uchida’s (8 April 1917 – 30 July 2013) strides to understand genetic diseases such as Down syndrome paved the way for early screening of chromosomal abnormalities in foetuses.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
Maggie Lim (5 January 1913 – November 1995) was a Singaporean physician who promoted family planning and expanded the access to clinics to improve the quality of life for mothers and children in Singapore’s early days.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
The founder of the Adyar Cancer Institute in India, Muthulakshmi Reddy (30 July 1886 – 22 July 1968), fought to uplift women and girls from impoverished situations.
Chinese-American virologist and molecular biologist Flossie Wong-Staal (27 August 1946 – 8 July 2020) was the first scientist to clone HIV and determine the function of its genes.
Maharani Chakravorty (1937 – 2015) was one of India’s earliest molecular biologists whose research paved the way for advances in the treatment of bacterial and viral infections.
Archana Sharma (16 February 1932 - 14 January 2008) conducted research into plant and human genetics that expanded the understanding of both botany and human health. In relation to botany, she uncovered the means by which asexually-reproducing plants evolve into new species.
The first Thai woman to receive a degree in medicine, Margaret Lin Xavier (29 May 1898 – 6 December 1932), is best remembered for her compassion towards her less privileged patients.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Filipino chemist and pharmacist Manuel A. Zamora (29 March 1870 – 9 July 1929) is best remembered for his discovery of the tiki-tiki formula to combat beriberi, a disease caused by Vitamin B1 deficiency.
After witnessing death and suffering as a youth in his home village during World War II, Nguyễn Tài Thu (6 April 1931 – 14 February 2021) set his sights on alleviating pain by becoming a doctor. After studying Traditional Chinese Medicine in China in the 1950s, Thu returned to Vietnam to serve in military hospitals. Eventually, he became the country’s foremost practitioner of acupuncture, a technique he first learned by inserting needles into himself.
David T. Wong (born 1936) is a Hong Kong-born American neuroscientist who is best known for discovering the antidepressant drug fluoxetine, better known as Prozac.
Indian organic chemist Asima Chatterjee (1917 to 2006) studied the medicinal properties of plant products, especially compounds known as vinca alkaloids.
Hsien Wu (24 November 1893 – 8 August 1959) is widely regarded as the founder of biochemistry and nutrition science in China. He was the first to propose that protein denaturation was caused by the unfolding of the protein, instead of chemical alteration.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Syed Qasim Mehdi (13 February 1941 – 28 September 2016) was a Pakistani molecular biologist who was a founding member of the Human Genome Diversity Project (HGDP), which assessed human diversity by studying human migration, mutation rates, relationships between different populations, genes involved in height and selective pressure.
Tsai-Fan Yu (1911 – 2 March 2007) was a Chinese-American physician and researcher who was the first female full professor at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. She discovered that gout, a condition characterized by the painful inflammation of joints, was caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the bloodstream.
Min Chueh Chang (10 October 1908 – 5 June 1991) was a Chinese-American biologist who studied fertilization in mammalian reproduction.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.