Science
News
04 Feb 2021
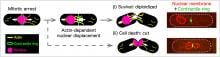
Cells replicate their genetic material and divide into two identical clones to perpetuate life. Some cells pause in the process with a single, undivided nucleus. When the cell resumes division after such a pause, the nucleus can become caught in the fissure, splitting violently, and killing both cells. But that is not always the case. Researchers from Hiroshima University in Japan are starting to understand how active nuclear displacement rescues cell death.
28 Jan 2021
A tick saliva study reveals immune responses that could lead to better protection for cattle.
24 Jan 2021
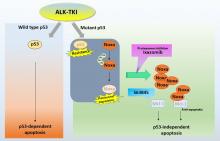
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in Clinical Cancer Research that in the most common type of lung cancer, certain secondary mutations occurring with another gene alteration known as ALK make the efficacy of alectinib, an otherwise commonly used drug for treating lung cancer, become unfavorable. Combining alectinib with another kind of drug can overcome this adverse effect, however.
22 Jan 2021
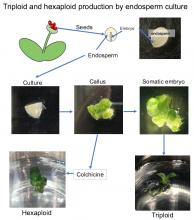
Scientists at Hokkaido University and Chiba University have developed simultaneous triploid and hexaploid varieties of Haemanthus albiflos by the application of endosperm culture, thus extending the use of this technique.
21 Jan 2021
A team of scientists in Japan has developed a novel method to induce stem cell generation from the blood samples of dogs. Through this technique, the scientists hope to advance regenerative therapies in veterinary medicine. This would mean that, in the near future, veterinarians might be able to reverse conditions in dogs that were previously thought incurable.
20 Jan 2021
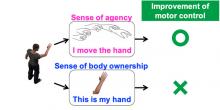
Patients with motor dysfunctions are on the rise across Japan as its population continues to age. A Tohoku University researcher has developed a new method of rehabilitation using virtual reality to increase the sense of agency over our body and aid motor skills.
18 Jan 2021
Researchers at Osaka City University use quantum superposition states and Bayesian inference to create a quantum algorithm, easily executable on quantum computers, that accurately and directly calculates energy differences between the electronic ground and excited spin states of molecular systems in polynomial time.
12 Jan 2021
An atomic switch is bringing us closer to highly effective solid-state batteries for electric vehicles.
11 Jan 2021
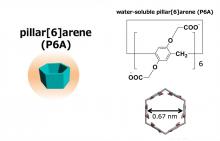
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in Communications Chemistry that a molecule known as pillar[6]arene can form a host–guest compound with a cancer-associated metabolite. The phenomenon can be used to efficiently detect the metabolite in crude biological samples, which is important for preventing and treating metabolic syndrome and associated pathologies.
07 Jan 2021
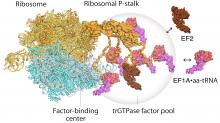
Factor-pooling by ribosomes caught on video using state-of-art high-speed atomic force microscopy technology.
28 Dec 2020
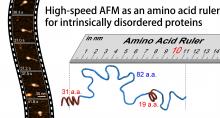
Kanazawa University’s pioneering high-speed atomic force microscope technology has now shed light on the structure and dynamics of some of life’s most ubiquitous and inscrutable molecules – intrinsically disordered proteins. The study is reported in Nature Nanotechnology.
28 Dec 2020
Investigations of a cellular protein have uncovered a possible link with schizophrenia.
28 Dec 2020
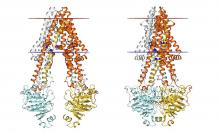
iCeMS scientists have revealed how a transporter protein twists and squeezes compounds out of cells, including chemotherapy drugs from some cancer cells.
25 Dec 2020
In their paper, the team described a novel scenario for PBH formation and showed that the black holes from the “multiverse” scenario can be found using the Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC) of the 8.2m Subaru Telescope, a gigantic digital camera—the management of which Kavli IPMU has played a crucial role—near the 4,200 meter summit of Mt. Mauna Kea in Hawaii.
24 Dec 2020
Tohoku University scientists have, for the first time, provided experimental evidence that cell stickiness helps them stay sorted within correct compartments during development. How tightly cells clump together, known as cell adhesion, appears to be enabled by a protein better known for its role in the immune system. The findings were detailed in the journal Nature Communications.
23 Dec 2020
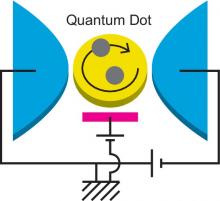
Osaka City University scientists have developed mathematical formulas to describe the current and fluctuations of strongly correlated electrons in quantum dots. Their theoretical predictions could soon be tested experimentally.
23 Dec 2020
A transporter protein that regulates cell membrane cholesterol likely played an important role in vertebrate evolution, according to a review published by iCeMS researchers in the journal FEBS Letters.
22 Dec 2020
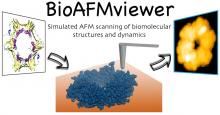
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) allows to obtain images and movies showing proteins at work, however with limited resolution. The developed BioAFMviewer software opens the opportunity to use the enormous amount of available high-resolution protein data to better understand experiments. Within an interactive interface with rich functionality, the BioAFMviewer computationally emulates tip-scanning of any biomolecular structure to generate simulated AFM graphics and movies. They greatly help in the interpretation of e.g., high-speed AFM observations.
21 Dec 2020
In the 1970s, physicists uncovered a problem with the Standard Model of particle physics—the theory that describes three of the four fundamental forces of nature (electromagnetic, weak, and strong interactions; the fourth is gravity). They found that, while the theory predicts that a symmetry between particles and forces in our Universe and a mirror version should be broken, the experiments say otherwise. This mismatch between theory and observations is dubbed “the Strong CP problem”—CP stands for Charge+Parity. What is the CP problem, and why has it puzzled scientists for almost half a century?
17 Dec 2020
A researcher at The University of Tokyo develops a method for recharging used N95 masks with a van de Graaff generator, which may greatly alleviate the lack of high-quality personal protective equipment during the COVID-19 pandemic
14 Dec 2020
Local development issues are often complex and involve multiple stakeholders, making them difficult to solve. IIUM transdisciplinary expert Irina Safitri Zen of the Sustainability Leadership for Community (SL4C) program says academics need to develop core competencies in order to translate local sustainability policies into actions.
14 Dec 2020
Scientists at The University of Tokyo study aluminosilicate glass to determine its complex local structure with unprecedented detail. This work may lead to tougher and more inexpensive glass for touchscreens and solar arrays
14 Dec 2020
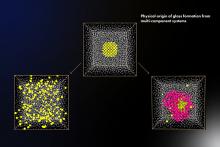
Scientists at The University of Tokyo use computer simulations to model the effects of elemental composition on the glass-forming ability of metallic mixtures, which may lead to tough, electroconductive glasses
11 Dec 2020
Recognizing species is important for understanding regional biodiversity and for environmental conservation. However, taxonomic identity is sometimes obscure even with the organisms that are closest to human life.
07 Dec 2020
A team of researchers understands more about the melting of the Greenland ice sheet. They discovered a flow of hot rocks, known as a mantle plume, rising from the core-mantle boundary beneath central Greenland that melts the ice from below.
02 Dec 2020
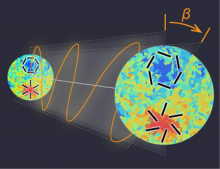
Yuto Minami at KEK and Eiichiro Komatsu at Kavli IPMU developed a new method to calibrate detectors to the light from dust in our Galaxy, thereby describing a new physics, with 99.2 percent accuracy, that may show parity symmetry breaking.
02 Dec 2020
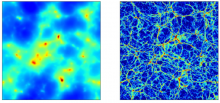
A research team including Kavli IPMU Principal Investigator Naoki Yoshida has, in a world first, succeeded in performing a 6-dimensional simulation of neutrinos moving through the universe.
01 Dec 2020
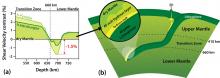
Researchers at Ehime University have recently measured the propagation speed of ultrasonic waves in an aluminum-rich hydrous mineral called Al-phase D at pressure conditions relevant to the Earth’s deep mantle. Their results suggest that seismic shear anomalies observed locally beneath subduction zones may reveal the presence of hydrous minerals in the uppermost lower mantle, which would have important implications for the Earth’s interior because hydrogen affects considerably the physical and chemical properties of mantle minerals.
25 Nov 2020
Materials that convert mechanical into electrical or magnetic energy could open the door to a future of wearable and structure-integrated virus sensors.
25 Nov 2020
A team of scientists has succeeded in visualizing how carbon dioxide (CO2) behaves in an ionic liquid that selectively absorbs CO2. The finding is expected to help develop more efficient methods to capture CO2 in the atmosphere, one of the major factors causing global warming.
Events

20 Aug 2005
This International conference will address issues on the rapid urbanisation in Asia including Urban development and process, Land use change, Urban regeneration, Population, Sustainable cities, World city development, Globalising cities in Asia

10 Aug 2005
Symposium highlights the growing role of Asian contribution to advances in Physics as well as to looks forward and assess the role of Physics in Engineering, Life Sciences and Technology in the next 100 years.

06 Sep 2005
this conference will bring together international speakers and delegates to discuss the latest developments in nanotechnology for healthcare

03 Jan 2006
93rd Indian Science Congress on "Integrated Rural Development:Science and Technology" from 3-7 January, Hyderabad, India
Giants in history
Turkish astrophysicist Dilhan Eryurt (29 November 1926 – 13 September 2012) conducted research on how the sun affects environmental conditions on the moon.
Chinese biochemist Chi Che Wang (1894 - 1979), one of the first Chinese women to study abroad, advanced to prominent research positions at American institutions including the University of Chicago and the Northwestern University Medical School.
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Chinese electron microscopy specialist Li Fanghua (6 January 1932 – 24 January 2020) facilitated the high-resolution imaging of crystal structures by eliminating interference.
Sálim Moizuddin Abdul Ali (12 November 1896 – 20 June 1987), commonly referred to as the Birdman of India, was the first person to conduct systematic surveys of birds from across India.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Angelita Castro Kelly (1942-2015) was the first female Mission Operations Manager (MOM) of NASA. She spearheaded and supervised the Earth Observing System missions during its developmental stage.
Malaysia’s first astrophysicist, Mazlan binti Othman (born 11 December 1951) was instrumental in launching the country’s first microsatellite, and in sending Malaysia’s first astronaut, Sheikh Muszaphar Shukor, into space.
Known as Mr. Natural Rubber, chemist and researcher B. C. Shekhar (17 November 1929 – 6 September 2006) introduced a number of technical innovations that helped put Malaysia’s natural rubber industry on the world map.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
South Korean theoretical physicist Daniel Chonghan Hong (3 March 1956 – 6 July 2002) achieved fame in the public sphere through his research into the physics of popcorn.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Chinese palaeontologist, archaeologist and anthropologist Pei Wenzhong (January 19, 1904 – September 18, 1982) is regarded as a founder of Chinese anthropology.
Physicist Narinder Singh Kapany (31 October 1926 – 4 December 2020) pioneered the use of optical fibres to transmit images, and founded several optical technology companies. Born in Punjab, India, he worked at a local optical instruments factory before moving to London for PhD studies at Imperial College. There, he devised a flexible fibrescope to convey images along bundles of glass fibres.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Charles Kuen Kao (Nov. 4, 1933 to Sept. 23, 2018) was an engineer who is regarded as the father of fibre optics. His work in the 1960s on long distance signal transmission using very pure glass fibres revolutionized telecommunications, enabling innovations such as the Internet.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Meghnad Saha (6 October 1893 – 16 February 1956) was an Indian astrophysicist best known for formulating the Saha ionization equation which describes the chemical and physical properties of stars.
Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose (30 November 1858 – 23 November 1937) was a scientist and inventor who contributed to a wide range of scientific fields such as physics, botany and biology.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (19 October 1910 – 21 August 1995) was an Indian astrophysicist who studied the structure and evolution of stars.
Joo-myung Seok (November 13, 1908 – October 6, 1950) was a Korean butterfly entomologist who made important contributions to the taxonomy of the native butterfly species in Korea.
Mathematician Maryam Mirzakhani (12 May 1977 – 14 July 2017) was the first and only woman and Iranian to date to win the Fields Medal in 2014 for her work on curved surfaces.
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (7 November 1888 – 21 November 1970) was an Indian physicist who performed ground-breaking research in the field of light-scattering.
Mohammad Abdus Salam (29 January 1926 – 21 November 1996) was a theoretical physicist and the first Pakistani to receive a Nobel Prize in science.
Srinivasa Ramanujan (22 December 1887 – 26 April 1920) was a math prodigy and widely considered one of India’s greatest mathematicians. Despite having almost no formal training in mathematics, he made substantial contributions to mathematical analysis, number theory, infinite series and continued fractions.
Gopalasamudram Narayanan Ramachandran (8 October 1922 – 7 April 2001) is best known for developing the Ramachandran plot to understand the structure of short chains of amino acids, known as peptides.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Chien-Shiung Wu (31 May 1912 – 16 February 1997) was an experimental physicist who made several important contributions to nuclear physics. Wu worked on the Manhattan Project – a top-secret program for the production of nuclear weapons during World War II and helped to develop a process for separating uranium into U235 and U238.
Meemann Chang (born 17 April 1936) is a Chinese palaeontologist who studied the fossils of ancient fish to understand the evolution of life. By examining fossils, she uncovered new insights on how vertebrates, animals with a backbone, migrated from the sea and became adapted to live on land.
Bibha Chowdhuri (1913 – 2 June 1991) was an Indian physicist who researched on particle physics and cosmic rays. In 1936, she was the only female to complete a M.Sc. degree at the University of Calcutta.
Lin Lanying (7 February 1918 – 4 March 2003) was a Chinese material engineer remembered for her contributions to the field of semiconductor and aerospace materials. Lanying was born into a family who did not believe in educating girls and she was not allowed to go to school.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater